Holliday junction-ZMM protein feedback enables meiotic crossover assurance.
2025 Nature
PMID: 40993383
Henggeler Adrian, Orlić Lucija, Velikov Daniel, Matos Joao
Waves of regulated protein expression and phosphorylation rewire the proteome to drive gametogenesis in budding yeast.
2024 Developmental cell;59(13):1764, 1782.e8, 1764-1782.e8.
PMID: 38906138
Wettstein Rahel, Hugener Jannik, Gillet Ludovic, Hernández-Armenta Yi, Henggeler Adrian, Xu Jingwei, van Gerwen Julian, Wollweber Florian, Arter Meret, Aebersold Ruedi, Beltrao Pedro, Pilhofer Martin, Matos Joao
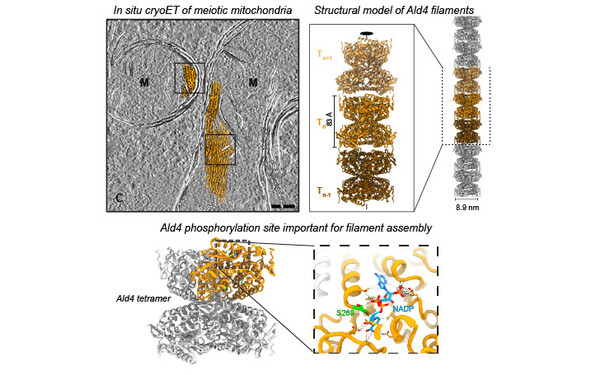
FilamentID reveals the composition and function of metabolic enzyme polymers during gametogenesis.
2024 Cell;187(13):3303, 3318.e18, 3303-3318.e18.
PMID: 38906101
Hugener Jannik, Xu Jingwei, Wettstein Rahel, Ioannidi Lydia, Velikov Daniel, Wollweber Florian, Henggeler Adrian, Matos Joao, Pilhofer Martin
Meiotic nuclear pore complex remodeling provides key insights into nuclear basket organization.
2023 The Journal of cell biology;222(2)
PMID: 36515990
King Grant A, Wettstein Rahel, Varberg Joseph M, Chetlapalli Keerthana, Walsh Madison E, Gillet Ludovic C J, Hernández-Armenta Claudia, Beltrao Pedro, Aebersold Ruedi, Jaspersen Sue L, Matos Joao, Ünal Elçin
The CDK1-TOPBP1-PLK1 axis regulates the Bloom's syndrome helicase BLM to suppress crossover recombination in somatic cells.
2022 Science advances;8(5):eabk0221.
PMID: 35119917
Balbo Pogliano Chiara, Ceppi Ilaria, Giovannini Sara, Petroulaki Vasiliki, Palmer Nathan, Uliana Federico, Gatti Marco, Kasaciunaite Kristina, Freire Raimundo, Seidel Ralf, Altmeyer Matthias, Cejka Petr, Matos Joao
Regulation of the MLH1-MLH3 endonuclease in meiosis.
2020 Nature(7830)
PMID: 32814904
Cannavo Elda, Sanchez Aurore, Anand Roopesh, Ranjha Lepakshi, Hugener Jannik, Adam Céline, Acharya Ananya, Weyland Nicolas, Aran-Guiu Xavier, Charbonnier Jean-Baptiste, Hoffmann Eva R, Borde Valérie, Matos Joao, Cejka Petr
Phosphorylation of the RecQ Helicase Sgs1/BLM Controls Its DNA Unwinding Activity during Meiosis and Mitosis.
2020 Developmental cell(6)
PMID: 32504558
Grigaitis Rokas, Ranjha Lepakshi, Wild Philipp, Kasaciunaite Kristina, Ceppi Ilaria, Kissling Vera, Henggeler Adrian, Susperregui Aitor, Peter Matthias, Seidel Ralf, Cejka Petr, Matos Joao
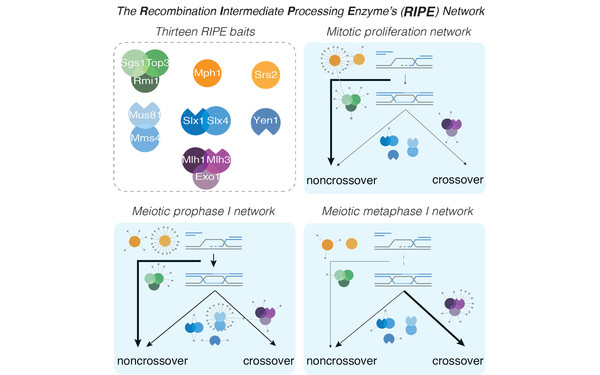
Network Rewiring of Homologous Recombination Enzymes during Mitotic Proliferation and Meiosis.
2019 Molecular cell(4)
PMID: 31351878
Wild Philipp, Susperregui Aitor, Piazza Ilaria, Dörig Christian, Oke Ashwini, Arter Meret, Yamaguchi Miyuki, Hilditch Alexander T, Vuina Karla, Chan Ki Choi, Gromova Tatiana, Haber James E, Fung Jennifer C, Picotti Paola, Matos Joao
Regulated Crossing-Over Requires Inactivation of Yen1/GEN1 Resolvase during Meiotic Prophase I.
2018 Developmental cell(6)
PMID: 29920281
Arter Meret, Hurtado-Nieves Vanesa, Oke Ashwini, Zhuge Tangna, Wettstein Rahel, Fung Jennifer C, Blanco Miguel G, Matos Joao
A Mechanism for Controlled Breakage of Under-replicated Chromosomes during Mitosis.
2016 Developmental cell(6)
PMID: 27997828
Duda Heike, Arter Meret, Gloggnitzer Jiradet, Teloni Federico, Wild Philipp, Blanco Miguel G, Altmeyer Matthias, Matos Joao
Dual control of Yen1 nuclease activity and cellular localization by Cdk and Cdc14 prevents genome instability.
2014 Molecular cell(1)
PMID: 24631285
Blanco Miguel G, Matos Joao, West Stephen C
Cell-cycle kinases coordinate the resolution of recombination intermediates with chromosome segregation.
2013 Cell reports(1)
PMID: 23810555
Matos Joao, Blanco Miguel G, West Stephen C
Regulatory control of the resolution of DNA recombination intermediates during meiosis and mitosis.
2011 Cell(1)
PMID: 21962513
Matos Joao, Blanco Miguel G, Maslen Sarah, Skehel J Mark, West Stephen C
Dbf4-dependent CDC7 kinase links DNA replication to the segregation of homologous chromosomes in meiosis I.
2008 Cell(4)
PMID: 19013276
Matos Joao, Lipp Jesse J, Bogdanova Aliona, Guillot Sylvine, Okaz Elwy, Junqueira Magno, Shevchenko Andrej, Zachariae Wolfgang
Monopolar attachment of sister kinetochores at meiosis I requires casein kinase 1.
2006 Cell(6)
PMID: 16990132
Petronczki Mark, Matos Joao, Mori Saori, Gregan Juraj, Bogdanova Aliona, Schwickart Martin, Mechtler Karl, Shirahige Katsuhiko, Zachariae Wolfgang, Nasmyth Kim