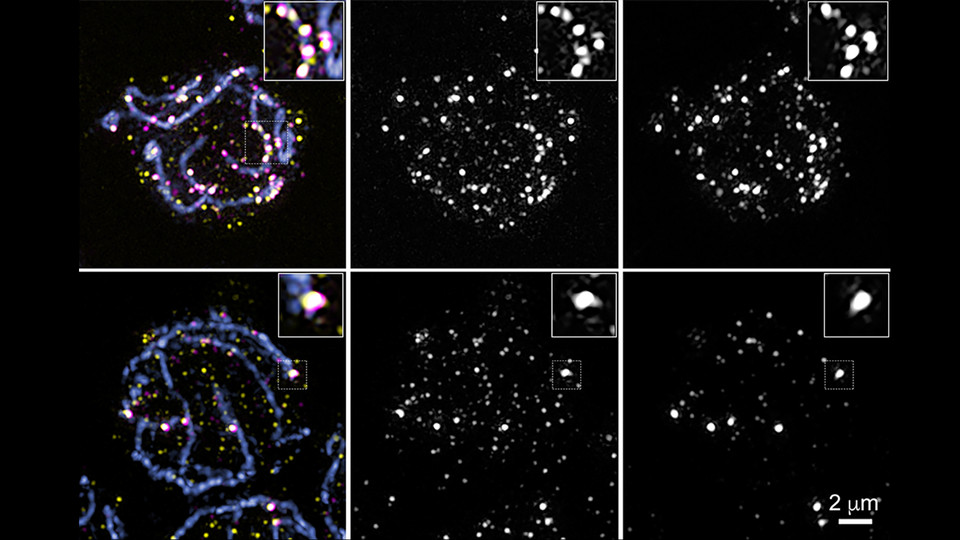

During the production of gametes, cells introduce DNA double strand breaks to facilitate the exchange of genetic material between maternal and paternal chromosomes, a process called crossing over. The number of breaks exceeds the final number of crossovers, with the remainder repaired as non-crossovers. TOP-3 is part of the BTR complex that can decatenate joint DNA molecules and reverse invading DNA strands, thereby mediating the non-crossover outcome and safeguarding chromosome integrity. “The function and mechanism of BTR has been studied in a variety of model organisms. However, biochemical reconstitution assays using mammalian proteins have so far omitted the ZnF domains”, says Verena Jantsch. “Consequently, the biological functions of these domains have been poorly characterized”.
Nina Vojtassakova, a diploma student and Rosaria Dello Stritto, a PhD student, engineered a mutant C. elegans lacking the TOP-3 ZnF domain. In contrast to the null mutant, viability was not affected. However, the authors observed an increased number of crossovers and a delay in the processing of recombination intermediates, hinting that the ZnF domain might be involved in reverting DNA strand invasions and/or resolution of catenated DNA strands by the BTR complex. The team could explain the milder phenotype by showing that the ZnF domain cooperates with another BTR protein, RMH-2, to localize the complex to early recombination intermediates and thus facilitate their processing. In doing so, TOP-3 also prevents recombination between heterologous DNA sequences, which can lead to dangerous chromosomal translocations.
The authors’ findings raise interesting questions about the role of the TOP3 ZnF domain during mitotic cell division, in which dysregulation of the BTR complex can lead to Bloom syndrome in humans, a disease characterized by genomic instability and increased susceptibility to cancer. “Using C. elegans, in which TOP-3 contains only one ZnF domain, we can now provide a better understanding of the importance of this highly conserved, but understudied domain in TOP3”, says Verena Jantsch. “Vertebrates, however, contain up to five of these domains. Our study thus may also provide incentives to study their function in more complex organisms, including humans”.
Publication:
Maria Rosaria Dello Stritto, Nina Vojtassakova, Maria Velkova, Patricia Hamminger, Patricia Ulm, Verena Jantsch: The topoisomerase 3 zinc finger domain cooperates with the RMI1 scaffold to promote stable association of the BTR complex to recombination intermediates in the Caenorhabditis elegans germline. Nucleic Acids Research 2022