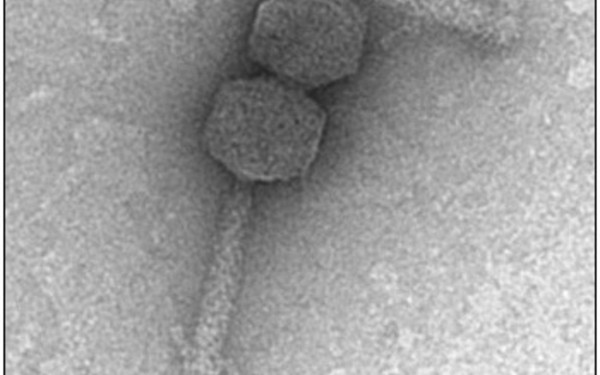
Spotlights
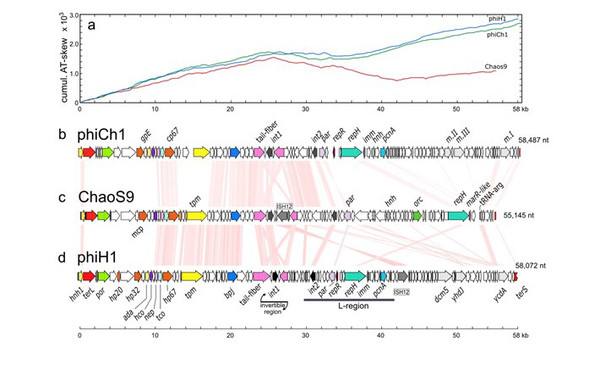
Genome map of ChaoS9 compared to φCh1 and φH1. (a) Cumulative AT-skew of all three virus genomes. (b) Genome map of phiCh1; (c) Genome map of ChaoS9; (d) Genome map of phiH1. Scale bar at bottom shows length, in kb. Pink shading between genome maps indicates similarity of encoded proteins (tBLASTx) at ≥ 30% amino acid identity level. Colour coding of genes indicates those encoding proteins with predicted (or experimentally determined) functions. Some of these genes are labeled along the gene maps.